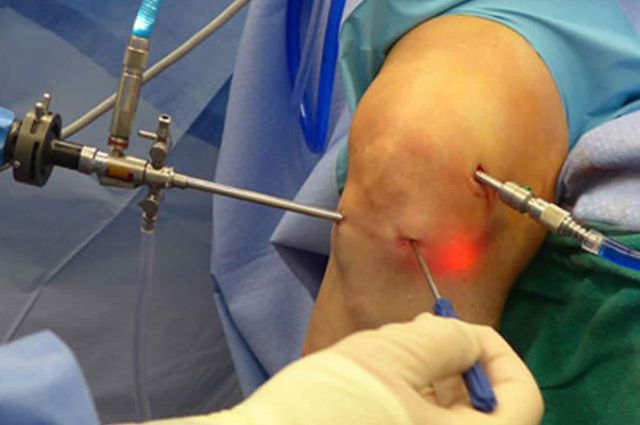
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat joint-related conditions and injuries. It involves the use of a specialized instrument called an arthroscope, which is a thin, flexible tube equipped with a tiny camera and surgical tools. During arthroscopy, a small incision is made near the affected joint, and the arthroscope is inserted to provide a clear view of the joint’s interior on a monitor. This allows surgeons to diagnose issues such as torn ligaments, damaged cartilage, or joint inflammation and perform various therapeutic procedures, including repairing damaged tissue or removing loose fragments. Arthroscopy is favored for its reduced surgical trauma, shorter recovery times, and minimal scarring compared to traditional open surgery, making it a valuable technique in orthopedic medicine, particularly for knee, shoulder, and hip problems.