Fracture and Trauma
Fracture and trauma refer to injuries to bones and soft tissues, often resulting from accidents, falls, sports injuries, or other forms of physical trauma. Here’s a brief description of these terms:
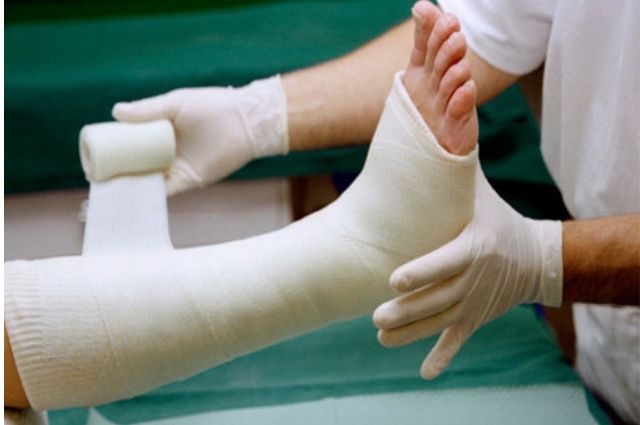
Fracture: A fracture is a medical term for a broken bone.
It can occur in various ways, such as a direct blow to the bone, a fall, twisting force, or repetitive stress on the bone.
Fractures can range in severity from hairline cracks (stress fractures) to complete breaks, where the bone is separated into two or more pieces.
Common types of fractures include open fractures (where the bone breaks through the skin) and closed fractures (where the skin remains intact).
Treatment of fractures typically involves realigning and stabilizing the bone, often through casting, splinting, or surgical intervention, depending on the nature and location of the fracture. Fractures require proper medical attention to ensure they heal correctly and to prevent complications like infection or long-term deformities.
Trauma: Trauma refers to physical injuries or damage to the body, which can affect not only bones but also soft tissues like muscles, tendons, ligaments, and organs. Trauma can result from a wide range of incidents, including car accidents, falls, sports injuries, assaults, and more.
Trauma can lead to various types of injuries, including fractures, dislocations, sprains, strains, contusions (bruises), and internal injuries.
The severity of trauma can vary widely, from minor injuries that heal with rest and self-care to life-threatening injuries requiring immediate medical attention.
Trauma management involves assessing the extent of injuries, stabilizing the patient, controlling bleeding, and providing appropriate treatment, which may include surgery, wound care, rehabilitation, or other interventions.
In some cases, trauma may also have psychological and emotional effects, necessitating counseling or mental health support for affected individuals.
Both fractures and trauma require prompt and appropriate medical evaluation and treatment to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients. Early intervention and comprehensive care can help reduce pain, promote healing, and minimize the risk of complications associated with these injuries.